Discrete time-trees:
theory and open problems
Alex Gavryushkin

(Joint work with Erick Matsen and Chris Whidden,
Fred Hutch Cancer Center, Seattle, WA, USA)
September 5, 2016
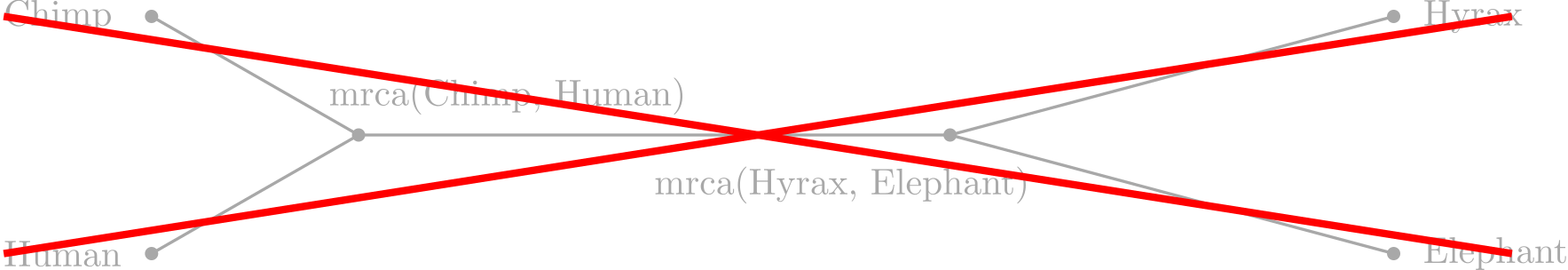
Phylogenetic tree

Not in this talk
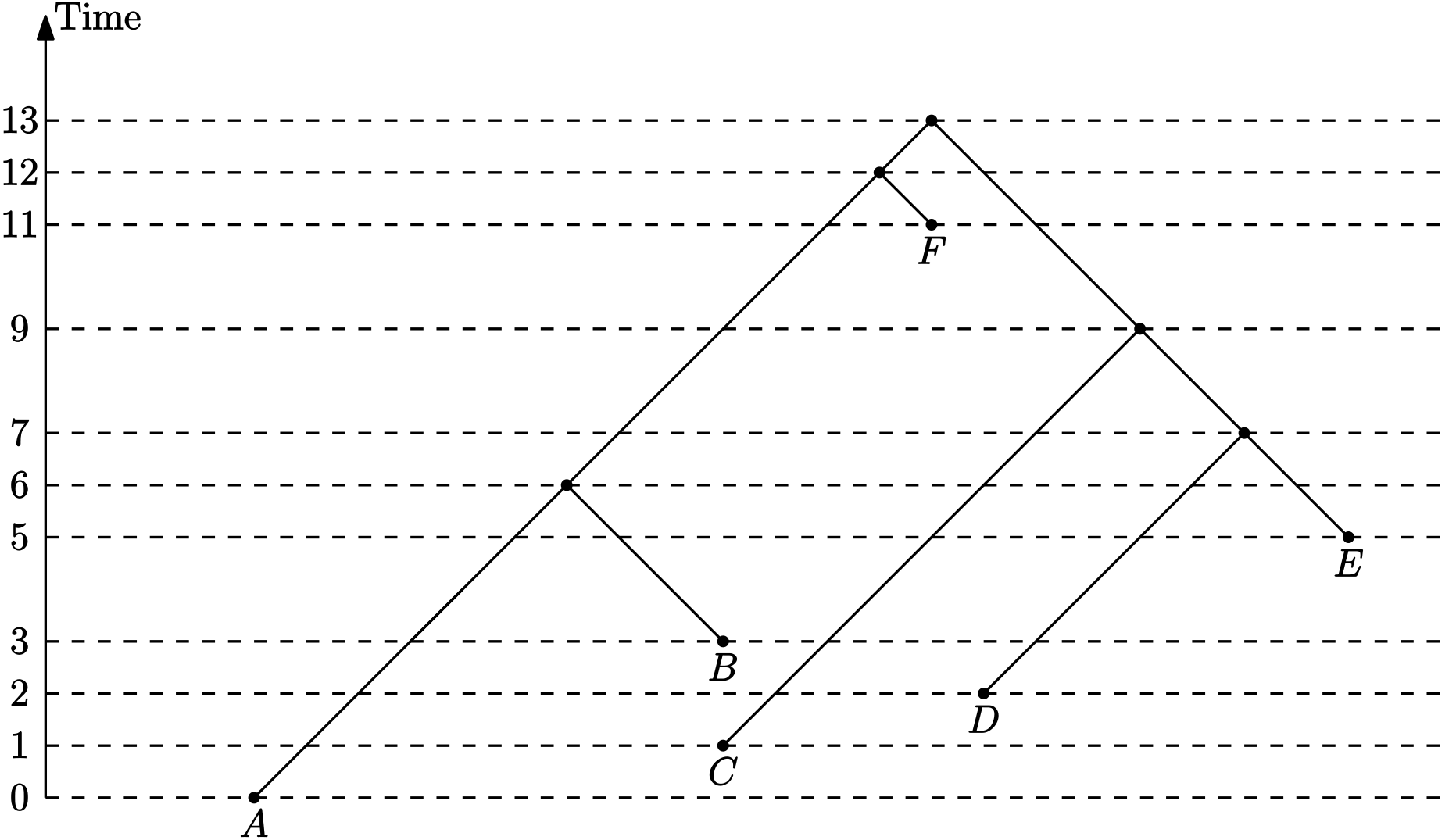
(Discrete) Time-tree
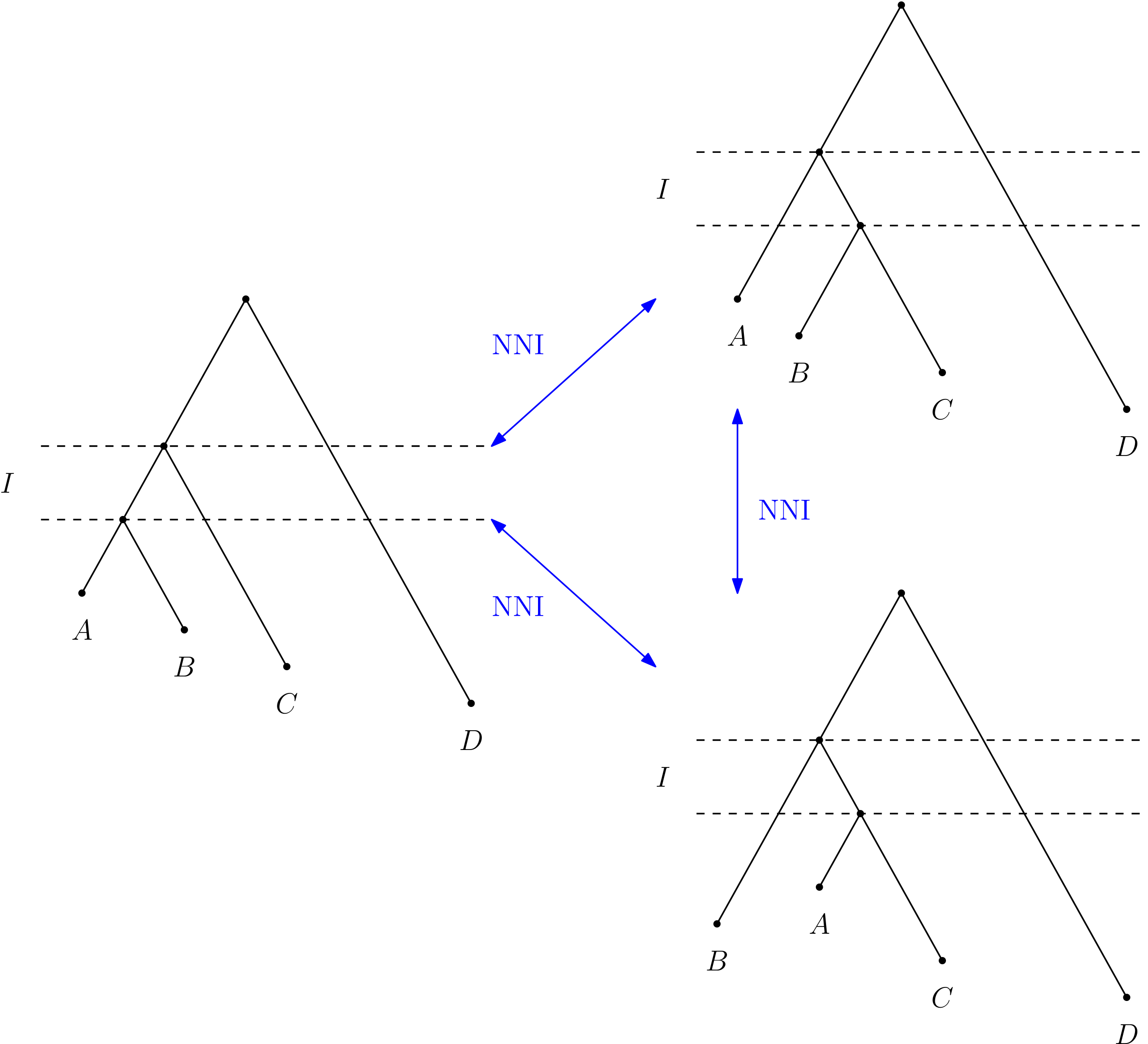
NNI graph
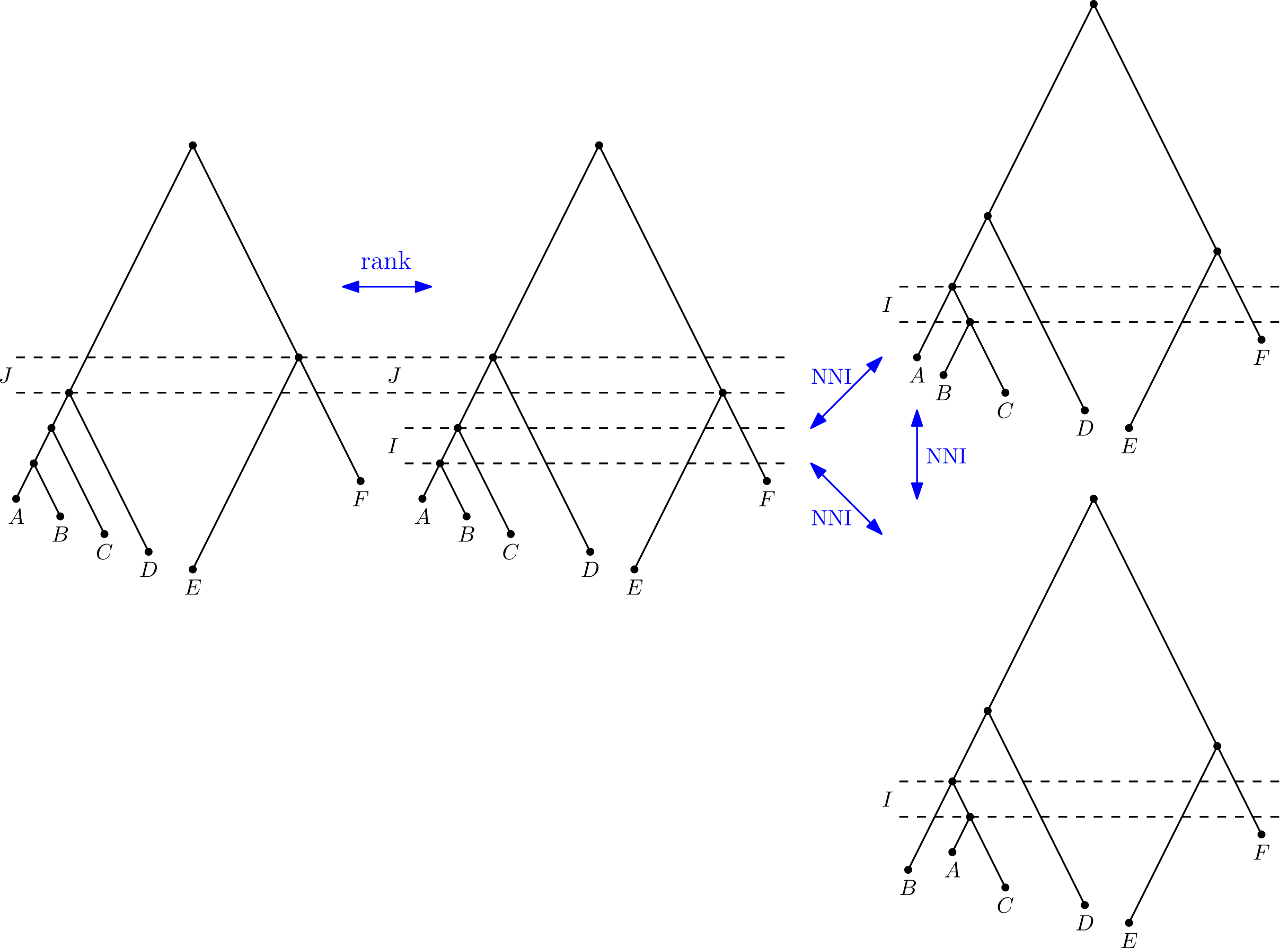
Discrete time-tree space
Graph = Metric

Trees at distance 2
Trees at distance 3
Main idea
(my failed proof)
History of the NNI graph
- Over 25 year of work!
- Over 7 erroneous papers published!
What's wrong with the NNI graph?
-
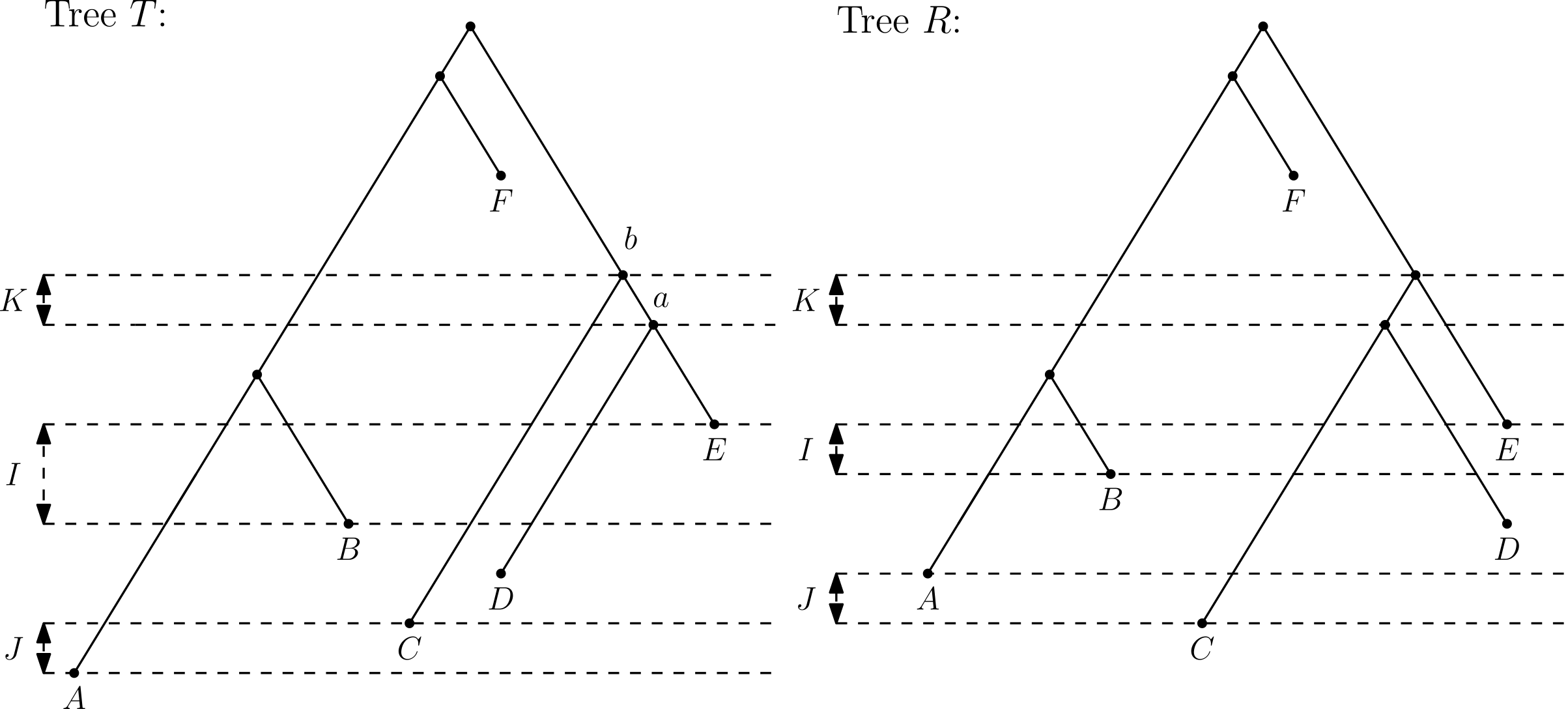
The Split Theorem
-
The merge and sort trick
Merge and sort trick
Merge and sort trick
RNNI is free from all these!
- Split theorem. Tick.
- Merge and sort doesn't work. Tick
-
Efficient polynomial algorithm?
What we've done?
-
Introduced the RNNI graph on ranked trees (to the best of our knowledge)
-
Established basic geometric properties of the graph
-
Proved that all the fancy NNI methods, e.g. Sleator-Tarjan-Thurston and merge-and-sort argument, don't work
-
Failed to prove that RNNI is polynomial-time decidable
What has to be done?
- Is RNNI polynomial? Complexity?
- Split Theorem
- Are these two related?
- ...
Why is this important?
- Tree search algorithms
- Model testing/selection and other simulation studies
Why is this hard?
Trees are many!
References:
- Li, Tromp, and Zhang. Some Notes on the Nearest Neighbour Interchange Distance. (1996)
- Dasgupta, He, Jiang, Li, Tromp, and Zhang. On Computing the Nearest Neighbor Interchange Distance. (1999)
- Sleator, Tarjan, and Thurston. Short Encodings of Evolving Structures. (1992)
- Gavryushkin and Drummond. The space of ultrametric phylogenetic trees. (2015)
- Gavryushkin, Whidden, and Matsen. The combinatorics of discrete time-trees: theory and open problems. (bioRxiv, 2016)